 Study of the effects of the natural variability of wood for optimized utilization of the forest resource and to improve the quality of thermally treated European wood
Study of the effects of the natural variability of wood for optimized utilization of the forest resource and to improve the quality of thermally treated European wood
PI : Philippe Gérardin (EA 4370 – Research Unit for the Study and Research of Wood Materials — LERMAB)
Co-applicant : Joint Research Unit for Forest and Wood Resource Studies —LERFOB
Collaboration: Anélie Petrissans, Mathieu Petrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Joël Hamada
________________________________________________________________
Context – The thermal treatment of wood by soft pyrolysis is a preservation process with low environmental impact constituting an alternative to the treatment of wood by impregnation of biocides. Depending on conditions of the treatment (time, temperature), the chemical composition of the different cell wall constituents is more or less modified influencing the properties of the material with regards to its durability to fungal attacks and its dimensional stability. One of the current barriers in developing this process on an industrial scale lies in the difficulty of making a product consistent in quality (durability, dimensional stability, color). No study currently exists which investigates the effects of the intrinsic properties of a given wood species on its behavior during thermal treatment.
Objectives – To investigate the effect of the initial intrinsic wood properties (density, chemical composition) directly linked to wood’s natural variability on its susceptibility to thermo-degradation occurring during heat treatment and properties conferred on the material contributing to the heterogeneity of the finished product as a raw material and that of the process itself. Such data could prove valuable towards improving industrial scale treatment processes generally conducted on a single wood species.
Approach —
We investigated how the natural variability of wood effects the wood’s polymers thermo-degradation and how these modifications modify wood properties on two different scales:
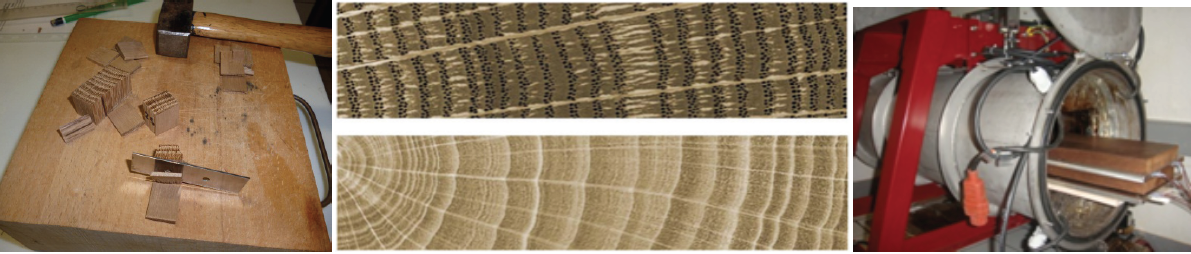
- a macroscopic scale performed on boards allowed us to characterize the effect of natural variability on the process, properties and performance of the heat treated materials. Boards were selected from different positions in the same tree and/or from trees with different sivicultural history to allow us to obtain boards with uniform density determined using X-ray tomography. The influence of the initial inter- and intra-tree heterogeneity on mass loss during the heat treatment process and the final product properties were both investigated.
- a small scale study performed on few mg of sawdust taken from within annual rings of the same cross section of trunk allowed us to study the effect of the intra-ring variability on wood thermal degradation. The sampling technique was used for different part of the wood: sapwood versus heartwood, earlywood versus latewood, and taken from different positions within the heartwood. Heat treatment was performed on small samples of sawdust using thermogravimetric analysis and thermodesorption coupled to gas chromatography and coupled to mass spectroscopy (TD-GC–MS) allowing us to evaluate the thermal behavior of each of tissue type. Obtained results will make it possible to propose recommendations towards improving the heat treatment process efficiency and ultimately will improve quality and homogeneity of heat treated materials.
The first part of this work was conducted on sessile oaks (Quercus petraea Liebl), and investigation is ongoing on fir trees (Abies alba).
Key results — Intra rings studies highlighted that for both species studied, European oak (Quercus petraea L.) and fir (Abies alba), earlywood was more susceptible to thermal degradation than latewood indicating that ring width could be an influencing parameter during heat modifications. In both cases, higher stability of latewood compared to earlywood was credited to higher cellulose content. At the same time, oak heartwood was also more susceptible to thermal degradation than sapwood. This behavior may be due to the higher extractives content of heartwood, which has been shown to be more susceptible to thermal degradation by TGA in the presence of the latter.
Main findings — Interspecies and intraspecies factors directly affect wood stability during thermal degradation. Intraspecific variability, such as radial position along the cross section, is also a key parameter in wood thermal degradation as demonstrated by the higher susceptibility of early versus latewood or heartwood versus sapwood.
Future perspectives — The obtained kinetic data of the thermo-degradation reaction will be used to improve modeling and simulation of the wood heat treatment by conduction in order to develop a prediction tool. Using results obtained by TGA, we will aim to predict overall weight loss of a board according to its earlywood / latewood ratio.
_______________________
Conferences :
J. Hamada, A. Pétrissans, F. Mothe, M. Fournier, M. Pétrissans, P. Gérardin. Effect of the natural density variability of the european oak on the quality of thermally treated wood material, Woodchem, September 26-27, 2013 Nancy, France.
J. Hamada, A. Pétrissans, F. Mothe, M. Pétrissans, P. Gérardin, Analysis of the effects of the European oak natural variability on the modification of the density distribution and chemical composition during the heat treatment, COST Actions FP0904 and FP1006, Characterization of modified wood in relation to wood bonding and coating performance“, October 16-18, 2013, Rogla, Slovenia.
A. Pétrissans, J. Hamada, M. Chaouch, M. Pétrissans, P. Gérardin Modeling and numerical simulation of wood torrefaction, vith international scientific and Technical Conference Innovations in Forest Industry and Engineering Design, INNO_2012, November 14-16, 2013, Yundola, Bulgaria.
J. Hamada, A. Pétrissans, F. Mothe, M. Pétrissans, P. Gérardin, Effects of the intra ring density and chemical composition variability of oak wood on the thermo-degradation kinetic’s behavior. 7th European Conference on Wood Modification, March 10 – 12, 2014, Lisbon, Portugal
Knowledge transfer :
- Effect of the natural density variability of the European oak on the quality of thermally treated wood material. Joel Hamada, Anélie Pétrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Mériem Fournier, Mathieu Pétrissans, Philippe Gérardin. Woodchem. September 26-27, 2013 Nancy, France (poster presentation)
- Analysis of the effects of the European oak natural variability on the modification of the density distribution and chemical composition during the heat treatment. Joel Hamada, Anélie Pétrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Mathieu Pétrissans, Philippe Gérardin. COST Actions FP0904 and FP1006 „Characterization of modified wood in relation to wood bonding and coating performance“, October 16-18, 2013, Rogla, Slovenia (poster presentation)
- Modeling and numerical simulation of wood torrefaction. Anélie Pétrissans, Joel Hamada, Frédéric Mothe, Mériem Fournier, Mathieu Pétrissans, Philippe Gérardin. vith international scientific and Technical Conference Innovations in Forest Industry and Engineering Design. INNO_2013. November 14-16, 2013, Yundola, Bulgaria (oral presentation)
- Modeling and numerical simulation of wood torrefaction. Anélie Pétrissans, Joel Hamada, Mounir Chaouch, Philippe Gérardin, Mathieu Pétrissans .MeMoWood, Nancy, France, 1-4 October 2013 (oral presentation)
- Effect of the natural variability of the oak wood density on the thermo-degradation reactions during heat treatment by mild pyrolysis. Joël Hamada, Anélie Pétrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Mathieu Pétrissans, Philippe Gérardin. Journées GDR Bois, Champs sur Marne 19-21/11/2013 (poster presentation)
- Effects of the intra ring density variability of the European Oak wood on the thermo-degradation kinetic’s behavior. Joël Hamada, Anélie Pétrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Mathieu Pétrissans, Philippe Gérardin. Seventh European Conference on Wood Modification, Lisbon, Portugal, March 10-12, 2014 (oral presentation)
- Improvement of an industrial process of wood heat treatment by conduction: X-ray tomography analysis of natural wood variability and the final product quality. Joël Hamada, Anélie Pétrissans, Frédéric Mothe, Mathieu Pétrissans and Philippe Gérardin. 21st International Congress of Chemical and Process Engineering CHISA 23-27 August 2014 Prague, Czech Republic (poster presentation)


